Opportunity to gain deeper insight into potential interaction between implants and body tissues through high-output benchtop screening.
Published : July 31 , 2017 / DOI : 10.1080/14686996.2017.1348872
The quality of the tissue-implant interface is key to the success of implant integration. High-output benchtop screening can help developers in assessing the complex interplay between biomaterials and the body to better prepare for clinical trials, highlights a review in the journal Science and Technology of Advanced Materials.
High-output screening aims to maximize the amount of consistent data and information from the minimum number of tests or specimens. One way to achieve this is to simulate the implant environment in more detail during benchtop tests. By enhancing the clinical relevance of in vitro results, medical device makers will gain deeper insight into the performance of their designs, making it more straightforward to select leading candidates. Identifying poor performers earlier in the pipeline could help bring down development costs and speed up the introduction of promising designs.
“This drastically reduces the time and effort required for clinical tests,” writes review author Michael Gasik, a researcher based at Aalto University Foundation in Finland.
To illustrate the concept, Gasik considers a dental implant, one of the most common types of implants worldwide, and advocates a simple biomechanical test for analyzing tissue implant quality.
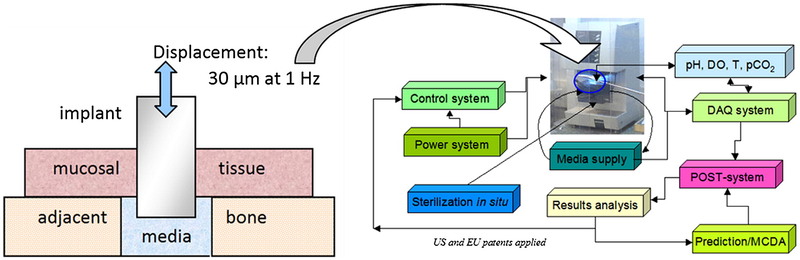
A dental implant test sample comprises a titanium post surrounded by cultured tissue. The supply of media to the sample is controlled to enable changes in temperature, acidity, and bacterial conditions. The post can be vibrated to mimic chewing, and mechanical measurements assess how firmly the implant is bound to the tissue.
For implants, study objectives include the identification of improved tissue-biomaterial adherence and resistance to bacterial contamination and biofilm formation. Gasik notes that test platforms can also be tailored for more complex scenarios such as articular cartilage repair.
For further information please contact:
Michael Gasik,
School of chemical engineering, Aalto University foundation, Finland
michael.gasik@aalto.fi
Journal information
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials (STAM), http://www.tandfonline.com/stam is an international open access journal in materials science. The journal covers a broad spectrum of topics, including synthesis, processing, theoretical analysis and experimental characterization of materials. Emphasis is placed on the interdisciplinary nature of materials science and on issues at the forefront of the field, such as energy and environmental issues, as well as medical and bioengineering applications
For more information about STAM please contact
Mikiko Tanifuji
Publishing Director
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials
E-mail: TANIFUJI.Mikiko@nims.go.jp
Information
- Authors
- Michael Gasik
- Citation
- Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater.18(2017)550.
- URL
- http://doi.org/10.1080/14686996.2017.1348872